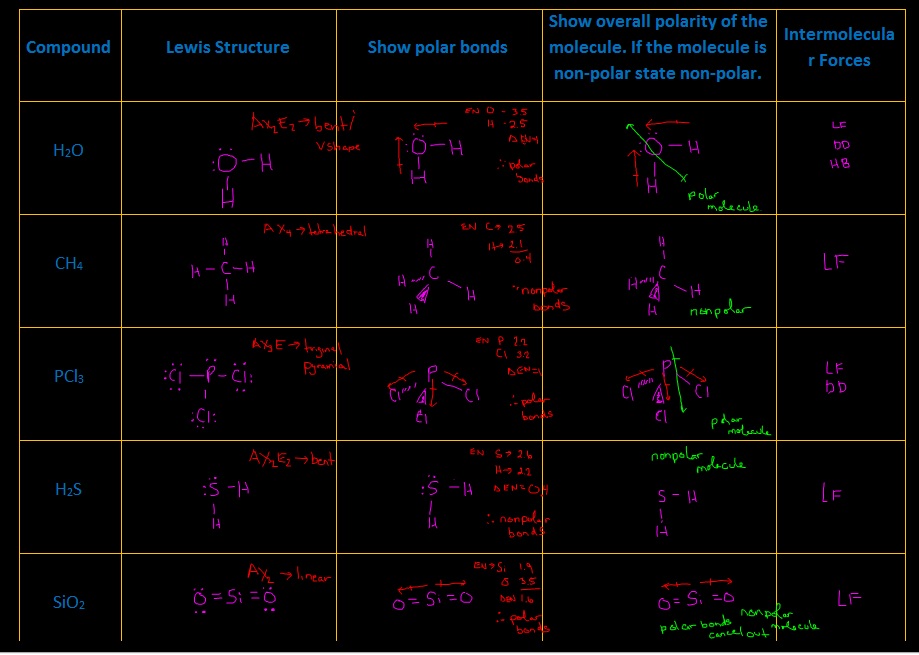
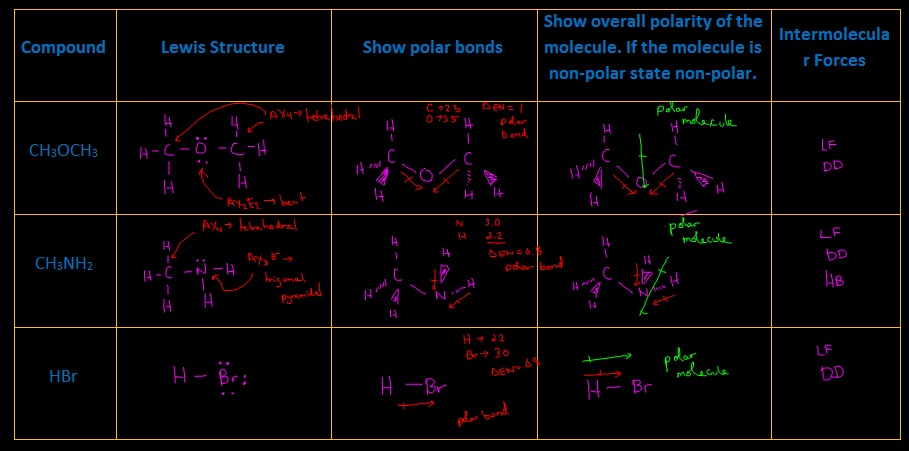
1.
What properties of ionic compounds suggest that ionic bonds are strong? Which of the representative elements tend to form positive ions? Which tend to form negative ions?
- Fact that ionic compounds are hard, brittle, and have high melting points and boiling points
- Metals tend to form positive ions and non-metals tend to form negative ions
2. How do electron dot diagrams of metal ions differ from those of non-metals? How are the electron dot diagrams of metal ions similar to those of non-metal ions?
- Electron dot diagrams of metal ions have no dots around them representing the fact that they lost electrons from their valence energy level
- Electron dot diagrams of non-metal ions have 8 dots around them representing the fact that they gained electrons to their valence energy level
- Both are in square brackets with their charge as a supercript
3.


5. Are the following pairs of atoms more likely to form an ionic or covalent bond? Explain your reasoning:
a. sulfur and oxygen – polar covalent - ΔEN = 0.8
b.
iodine and iodine – pure covalent - ΔEN = 0
c.
calcium and chlorine – ionic - ΔEN = 2.2
d.
boron and iodine – polar covalent - ΔEN = 0.7
e.
potassium and bromine – ionic - ΔEN = 2.2
6. Distinguish between bonding electrons and lone pair electrons.
- Bonding pair electrons are shared between two atoms involved in a covalent bond
- Lone pair electrons belong to one element
7. Compound A is formed when the element with the atomic number 3 combines with the element of atomic number 9. Compound B is formed when the element with atomic number 7 combine with the element with atomic number 9.
a. Compare the properties of compound A and B.
b. What type of compounds are A and B. Give reasons for your answer.
- Compound A is an ionic compound (element with atomic number 3 is Li combines with the element with atomic number 9 F has a ΔEN of 3.0). Therefore it will have a high mp and bp, form an electrolyte then added to water, and is a hard brittle crystal soli at room temp.
- Compound B is a polar covalent compound (Element with atomic number 7 is N and atomic number 9 is F - ΔEN = is 1.0 which makes it a polar bond. Also, when looking at shape we will see that its shape is triginal pyramidal and thus the polar bonds do not cancel out. Therefore, it most likely will be a liquid at room temp wit a mp / bp much lower than Compound A.
c. Clearly chow the structure of each compound formed, using electron dot diagrams and Lewis structures.

- Which type of bond – ionic, covalent, or polar covalent – will form between each of the following pairs of atoms? If the bond is polar, use arrows to show the direction of the dipole moment (Electronegativity values are on the Periodic Table at the back of your text books).
- H and Cl: polar covalent (arrow towards Cl)
- Si and O: polar covalent (arrow towards O)
- Mg and Cl: ionic
- Li and O: ionic
- N and O: polar covalent (arrow towards O)
- O and O: pure covalent
- I and Cl: pure covalent
- Cr and O: polar covalent (arrow towards O)
- C and Cl: polar covalent (arrow towards Cl)
9. Both boron and phosphorus form compounds with chlorine which involves 3 chlorine atoms bonded to a central atom (boron or phosphorus).
a. Classify each of these compounds as ionic or covalent. Justify your answer.
- Boron chloride – covalent compound (ΔEN is 1.2 giving it a polar bond, but its shape cancels out the polar bonds)
- Phosphorus trichloride – polar covalent compound (ΔEN is 1.0 giving it a polar bond, and its shape does not cancel out the polar bonds
b. How are the B – Cl bonds and N – Cl bonds similar? How are they different?
- both covalent bonds involving sharing of the electron pair in the bond
- B – Cl bond is a polar covalent bond – unequal sharing of the bonding pair electrons
- N – Cl bond is a pure covalent bond – equal sharing of the bonding pair electrons
c. What other properties can you predict for the two compounds? Use the concepts of electronegativity and Lewis structures to justify your answers.
- They will have state differences, with the P-Cl compound having a much higher bp / mp bcz it will have more IMF (LF and DD) versus the B – Cl compound (LF only)

10. A forensic scientist was given samples of four unknown solutions, the identity of which could affect the outcome of a court case involving electrocution. The chemist had reason to believe that the four substances were KCl (aq), C2H5OH (aq), HCl (aq), and Ba(OH)2 (aq). The investigation was designed to identify the chemicals and the following data was collected:
Solution |
Conductivity |
Litmus |
water |
none |
no change |
1 |
high |
no change |
2 |
high |
blue to red |
3 |
none |
no change |
4 |
high |
red to blue |
a. Idenify each of the solutions as either KCl (aq), C2H5OH (aq), HCl (aq), and Ba(OH)2 (aq). Justify your answer for each.
b. Why was water used to prepare the solutions also tested?
c. Which of the solutions could have been involved in somebody being electrocuted? Explain.
- Solution 1 – ionic compound(KCl): forms an electrolyte but does not affect litmus
- Solution 2 – acid (HCl): acids form an electrolyte and also caused blue litmus to turn red
- Solution 3 – covalent compound (C2H5OH): covalent compounds do not form electrolytes
- Solutions 4 – base (Ba(OH)2): bases form an electrolyte and also causes red litmus to turn blue
- Water was tested so that we know that any positive results (conductivity or litmus colour change) is due to the compounds dissolved in it and not the water itself
Any of the solutions except for solution 3 could be used to electrocute somebody as they will all form an electrolyte