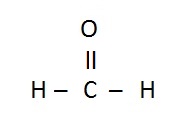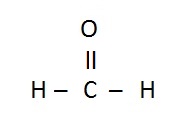Lewis Structure
The key ideas of the Lewis theory of bonding are:
- Atoms and ions are stable if they have a noble gas-like electron structure; i.e., a stable octet of electrons.
- Electrons are most stable when they are paired.
- Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve a stable octet of electrons.
- A stable octet may be achieved by an exchange of electrons between metal and nonmetal atoms.
- A stable octet of electrons may be achieved by the sharing of electrons between nonmetal atoms.
- The sharing of electrons results in a covalent bond
Writing Lewis Formulas
- Select a reasonable (symmetrical) “skeleton” for the molecule or polyatomic ion.
- The least electronegative element is usually the central element, except that H is never the central element, because it forms only one bond. The least electronegative element is usually the one that needs the most electrons to fill its octet.
- Oxygen atoms do not bond to each other except in (1) O2 and O3 molecules; (2) hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, and its derivatives, the peroxides, which contain the O22- group; and (3) the rare superoxides, which contain the O2- group.
- In ternary oxoacids, hydrogen usually bonds to an O atom, not to the central atom.
- For ions or molecules that have more than one central atom, the most symmetrical skeletons possible are used.
- Calculate Required, the number of valence (outer) shell electrons needed by all atoms in the molecule or ion to achieve noble gas configurations. Remember that some elements can have a compressed octet (eg. Be/B) and some elements can have an expanded octet (eg. P/S).
Calculate Have, the number of electrons available in the valence (outer) shells of all the atoms. For negatively charged ions, add to this total the number of electrons equal to the charge on the anion; for positively charged ions, subtract the number of electrons equal to the charge on the cation.
- Calculate the number of bonds by subtracting the have from required and dividing by 2.
Number of Bonds = (Required – Have)/2
Lewis formulas may be shown as either dot formulas or dash formulas.
- Determine the number of lone pair electrons.
Lone pair = Have – 2(Number of Bonds)
- Add single bonds to skeleton between all atoms. If any bonds are remaining add a double bond.
- Place lone pair electrons around atoms so that each atoms has an octet (or the correct number of electrons for their expanded or compressed octet).
| Example: CH2O |
| Element |
Have |
Required |
|
| C |
4 |
8 |
# bonds = (req'd - have) / 2
= (20 - 12) / 2
= 4 |
| H |
1(2) |
2(2) |
| O |
6 |
8 |
| total |
12 |
20 |
# of electrons in lone pair = have - 2(# bonds)
= 12 - 2(4)
= 4
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Step 1: Place the atoms around the central atom |
 |
| Step 2: Add bonds, single bonds first |
 |
| .....then double bond if there are still bonds left to place |
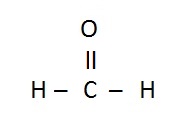 |
| Step 3: Add lone pair electrons |
 |
| Example: BO33- |
| Element |
Have |
Req'd |
|
| B |
3 |
6 |
# bonds = (req'd - have)/2
= (30 - 24)/2
= 3
|
| O |
6(3) |
8(3) |
| total |
21 + 3
= 24 |
30 |
| |
|
# of electron in lp
= have - 2(#bonds)
= 24 - 3(6)
= 18 |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Step 1: Place the atoms around the central atom |
 |
| Step 2: Add bonds, single bonds first |
 |
| Step 3: Add lone pair electrons |
 |
| Step 4: Add square brackets since it is an ion |
 |
| Example: PCl5 |
| Element |
Have |
Req'd |
# bonds = (req'd - have)/2
= (50 - 40)/2
= 10 |
| P |
5 |
10 |
| Cl |
7(5) |
8(5) |
| total |
40 |
50 |
# of electron in lp
= have - 2(#bonds)
= 24 - 3(6)
= 18 |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Step 1: Place the atoms around the central atom |
 |
| Step 2: Add bonds, single bonds first |
 |
| Step 3: Add lone pair electrons |
 |
| |
|