Example: CO2
![]()
Molecular Shape:
![]()
General Formula:
AX2
Shape Name:
Linear
Bond Angle(s):
180o
Example: BCl3

Molecular Shape:
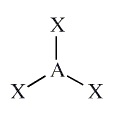
General Formula:
AX3
Shape Name:
trigonal planar
Bond Angle(s):
120o
Example: SO2

Molecular Shape:

Generic Formula:
AX2E
Shape Name:
bent or angular
Bond Angles:
<120o
Example: CH4

Molecular Shape:

General Formula:
AX4
Shape Name:
tetrahedral
Bond Angle(s):
109o
Example: NH3

Molecular Shape:

General Formula:
AX3E
Shape Name:
trigonal pyramidal
Bond Angle(s):
107o
Example: H2O

Molecular Shape:
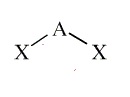
General Formula:
AX2E2
Shape Name:
bent or angular
Bond Angle(s):
<107o
Example: PCl5

Molecular Shape:

General Formula:
AX5
Shape Name:
triginal bipyramidal
Bond Angles:
90o, 120o, 180o
Example: SeCl4

Molecular Shape:
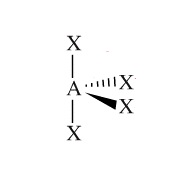
General Formula:
AX4E
Shape Name:
triginal bipyramidal
Bond Angles:
<90o
Example: BrF5

Molecular Shape:

General Formula:
AX3E2
Shape Name:
triginal bipyramidal
Bond Angles:
<90o
Example:
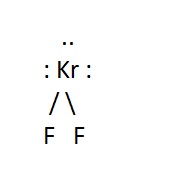
Molecular Shape:
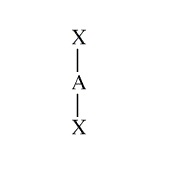
General Formula:
AX2E3
Shape:
linear
Bond Angle:
180o
Example:SF6

Moleculare Shape:
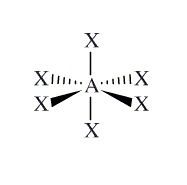
General Formula:
AX6
Shape Name:
octahedral
Bond Angles:
90o
Example: IF4

Moleculare Shape:

General Formula:
AX5E
Shape Name:
square pyramidal
Bond Angles:
<90o
Example: XeF4

Moleculare Shape:
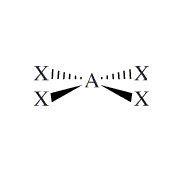
General Formula:
AX4E2
Shape Name:
square planar
Bond Angles:
<90o
Example:
Moleculare Shape:

General Formula:
AX3E3
Shape Name:
t-shape
Bond Angles:
<90o
Example:
Moleculare Shape:
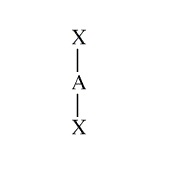
General Formula:
AX2E4
Shape Name:
linear
Bond Angles:
180o